Hypertension
To diagnose high blood pressure, your health care provider examines you and asks questions about your medical history and any symptoms. Your provider listens to your heart using a device called a stethoscope.
Your blood pressure is checked using a cuff, usually placed around your arm. It’s important that the cuff fits. If it’s too big or too small, blood pressure readings can vary. The cuff is inflated using a small hand pump or a machine.
Blood pressure measurement
A blood pressure reading measures the pressure in the arteries when the heart beats (top number, called systolic pressure) and between heartbeats (bottom number, called diastolic pressure). To measure blood pressure, an inflatable cuff is usually placed around the arm. A machine or small hand pump is used to inflate the cuff. In this image, a machine records the blood pressure reading. This is called an automated blood pressure measurement.
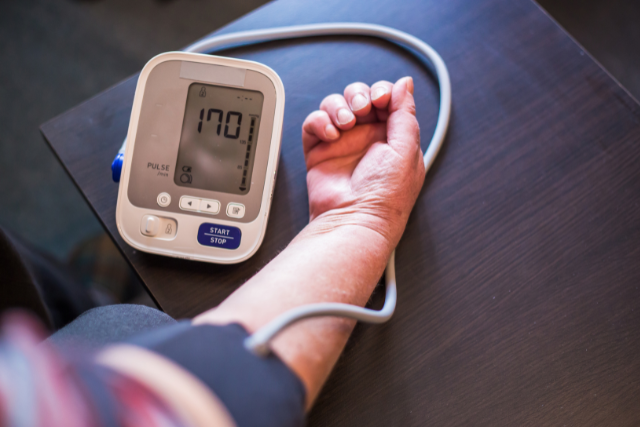
The first time your blood pressure is checked, it should be measured in both arms to see if there’s a difference. After that, the arm with the higher reading should be used.
Blood pressure is measured in millimeters of mercury (mm Hg). A blood pressure reading has two numbers.
- Top number, called systolic pressure. The first, or upper, number measures the pressure in the arteries when the heart beats.
- Bottom number, called diastolic pressure. The second, or lower, number measures the pressure in the arteries between heartbeats.
High blood pressure (hypertension) is diagnosed if the blood pressure reading is equal to or greater than 130/80 millimeters of mercury (mm Hg). A diagnosis of high blood pressure is usually based on the average of two or more readings taken on separate occasions.
Blood pressure is grouped according to how high it is. This is called staging. Staging helps guide treatment.
- Stage 1 hypertension. The top number is between 130 and 139 mm Hg or the bottom number is between 80 and 89 mm Hg.
- Stage 2 hypertension. The top number is 140 mm Hg or higher or the bottom number is 90 mm Hg or higher.
Sometimes the bottom blood pressure reading is normal (less than 80 mm Hg) but the top number is high. This is called isolated systolic hypertension. It’s a common type of high blood pressure in people older than 65.